Adapter Design Pattern
Structural: Adapter Pattern
What is an adapter design pattern?
View Answer:
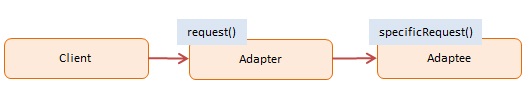
The objects participating in this pattern are:
Client -- In example code: the run() function
- calls into Adapter to request a service
Adapter -- In example code: ShippingAdapter
- implements the interface that the client expects or knows
Adaptee -- In example code: AdvancedShipping
- the object being adapted
- has a different interface from what the client expects or knows
class SimpleEarphones {
constructor() {
this.attach = function () {
console.log('Use Earphones with Type C phone');
};
}
}
// Adapter
class EarPhoneAdapter extends SimpleEarphones {
constructor(typeCphone) {
super();
this.attach = function () {
typeCphone.attach();
};
}
}
class TypeCPhone {
constructor() {
this.attach = function () {
console.log('Earphones attached to Type C phone');
};
}
}
let typeCphone = new TypeCPhone();
let adapter = new EarPhoneAdapter(typeCphone);
adapter.attach();
/*
Output:
Earphones attached to Type C phone
*/

// old interface
function Shipping() {
this.request = function (zipStart, zipEnd, weight) {
// ...
return '$49.75';
};
}
// new interface
function AdvancedShipping() {
this.login = function (credentials) {
/* ... */
};
this.setStart = function (start) {
/* ... */
};
this.setDestination = function (destination) {
/* ... */
};
this.calculate = function (weight) {
return '$39.50';
};
}
// adapter interface
function ShippingAdapter(credentials) {
var shipping = new AdvancedShipping();
shipping.login(credentials);
return {
request: function (zipStart, zipEnd, weight) {
shipping.setStart(zipStart);
shipping.setDestination(zipEnd);
return shipping.calculate(weight);
},
};
}
function run() {
var shipping = new Shipping();
var credentials = { token: '30a8-6ee1' };
var adapter = new ShippingAdapter(credentials);
// original shipping object and interface
var cost = shipping.request('78701', '10010', '2 lbs');
console.log('Old cost: ' + cost);
// new shipping object with adapted interface
cost = adapter.request('78701', '10010', '2 lbs');
console.log('New cost: ' + cost);
}
run();
/*
OUTPUT:
Old cost: $49.75
New cost: $39.50
*/
The Adapter pattern belongs to which pattern category?
View Answer:
What problem does the Adapter Pattern solve?
View Answer:
What is the Adapter Pattern's most noticeable feature?
View Answer:
What Pros and Cons can you think of regarding the Adapter Pattern?
View Answer:
Benefits
- Based on SOLID principles.
- We can add new adapters without breaking existing code.
- The code is both reusable and adaptable.
- Clean code — because the client/context does not use a different interface in each concrete class and can switch between additional adapters using polymorphism.
- Single Responsibility Principle - The principle of single responsibility. You can separate the interface or data conversion code from the main business logic of the program.
- Open/Closed Principle. If they interact with the adapters via the client interface, you can start introducing new kinds of adapters into the application without having to break the existing client code.
Drawbacks
- The overall complexity of the code rises as a result of the addition of new interfaces and classes. Changing the service class to match the rest of your code is sometimes easier.
When should the Adapter Pattern be used?
View Answer:
- There is a class whose interfaces do not match the one you need.
- There are several subclasses, but it’s impractical to adapt their interface by sub-classing every one.
In JavaScript, Are there any alternatives to using the adapter pattern?
View Answer:
How does the Adapter Pattern maintain the principle of single responsibility?
View Answer:
Can the Adapter Pattern be used with legacy code?
View Answer:
Is the Adapter Pattern the same as the Decorator Pattern?
View Answer:
What are the key components of the Adapter Pattern?
View Answer:
// Target Interface
class Target {
request() {
throw new Error('request() method must be implemented.');
}
}
// Adaptee
class Adaptee {
specificRequest() {
console.log('Adaptee specific request');
}
}
// Adapter
class Adapter extends Target {
constructor(adaptee) {
super();
this.adaptee = adaptee;
}
request() {
this.adaptee.specificRequest();
}
}
// Client
function clientCode(target) {
target.request();
}
// Usage
const adaptee = new Adaptee();
const adapter = new Adapter(adaptee);
clientCode(adapter);
In this example, we have a Target class representing the target interface. The Adaptee class represents the existing object with an incompatible interface. The Adapter class extends the Target class and internally uses the Adaptee object to bridge the gap between the target interface and the adaptee.
When the clientCode function is called with the adapter object, it calls the request method on the adapter. Internally, the adapter delegates the request to the Adaptee object by calling its specificRequest method. This allows the client to use the Adapter object as if it were a Target object, even though the underlying implementation comes from the Adaptee.
Note that this is a simplified example to demonstrate the concept of the Adapter Pattern in JavaScript. In a real-world scenario, the Adapter may need to perform additional logic or transformation to adapt the interface of the adaptee to the target interface.
What’s the difference between object and class adapter patterns?
View Answer:
1. Object Adapter Pattern:
- In this pattern, the adapter object contains an instance of the adaptee object and implements the target interface. It uses composition to "adapt" the adaptee's interface to the target interface.
- The adapter object wraps the adaptee object and translates the calls from the target interface to the adaptee's interface.
Here's an example:
// Target Interface
class Target {
request() {
throw new Error('request() method must be implemented.');
}
}
// Adaptee
class Adaptee {
specificRequest() {
console.log('Adaptee specific request');
}
}
// Object Adapter
class ObjectAdapter extends Target {
constructor(adaptee) {
super();
this.adaptee = adaptee;
}
request() {
this.adaptee.specificRequest();
}
}
// Client
function clientCode(target) {
target.request();
}
// Usage
const adaptee = new Adaptee();
const adapter = new ObjectAdapter(adaptee);
clientCode(adapter);
In this example, the ObjectAdapter class adapts the Adaptee object by containing an instance of it (this.adaptee). It implements the Target interface and internally delegates the request to the Adaptee object.
2. Class Adapter Pattern:
- In this pattern, the adapter class extends both the target class and the adaptee class. It uses multiple inheritance to "adapt" the adaptee's interface to the target interface.
- The adapter class directly inherits the functionality and properties from the adaptee class, while also implementing the target interface.
Here's an example:
// Target Interface
class Target {
request() {
throw new Error('request() method must be implemented.');
}
}
// Adaptee
class Adaptee {
specificRequest() {
console.log('Adaptee specific request');
}
}
// Class Adapter
class ClassAdapter extends Adaptee {
request() {
this.specificRequest();
}
}
// Client
function clientCode(target) {
target.request();
}
// Usage
const adapter = new ClassAdapter();
clientCode(adapter);
In this example, the ClassAdapter class extends both the Adaptee class and implements the Target interface. It directly inherits the specificRequest method from the Adaptee class and also implements the request method defined by the Target interface.
Both the Object Adapter Pattern and the Class Adapter Pattern achieve the same goal of adapting the interface of the adaptee to the target interface. The choice between the two depends on the specific requirements and constraints of your project.